Mutual funds are one of the most popular investment vehicles for individuals looking to grow their wealth in the financial markets. Offering a simple and efficient way to diversify a portfolio, mutual funds provide opportunities for investors to access a range of asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and money market instruments. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced investor, understanding the fundamentals of mutual funds is crucial for making informed decisions and achieving your long-term financial goals.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about mutual funds, including their structure, types, benefits, and risks. It will also provide tips for selecting the right mutual funds and answer common questions to help you navigate the world of mutual fund investing.
Key Takeaways
- Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to create a diversified portfolio managed by professional fund managers.
- There are several types of mutual funds, including equity, bond, money market, and balanced funds, each catering to different risk profiles.
- Mutual funds offer benefits such as diversification, liquidity, and professional management but also come with risks, such as market volatility and management errors.
- When selecting a mutual fund, consider factors such as your investment goals, risk tolerance, fees, and the fund manager’s experience.
- Regularly monitor your investments and adjust your portfolio as needed to stay on track with your financial objectives.
By following these guidelines, you can make informed decisions and invest in mutual funds with confidence to build your wealth over time.
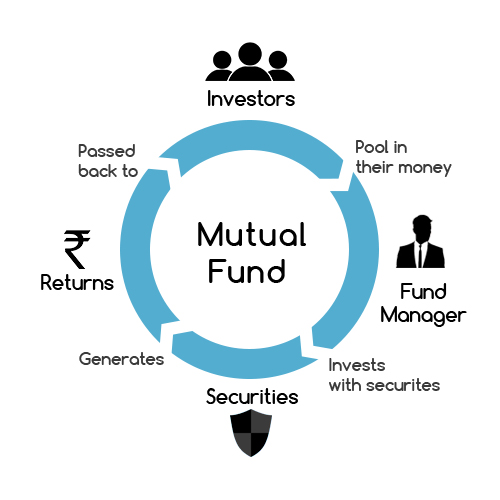
What is a Mutual Fund?
At its core, a mutual fund is a pool of money collected from many investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. These securities can include stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and more. The mutual fund is managed by a professional fund manager or a team of experts who make decisions on behalf of the fund’s investors.
By pooling money together, individual investors are able to access a more diversified portfolio than they might be able to create on their own. This diversification can help spread risk and potentially lead to more stable returns over time.
Key Components of Mutual Funds
Before diving deeper into mutual funds, it’s essential to understand some of the key components that make up these investment products:
- Net Asset Value (NAV): NAV refers to the value of a mutual fund’s assets minus its liabilities. It is typically calculated at the end of each trading day and represents the price at which investors buy or sell shares of the fund.
- Expense Ratio: The expense ratio is the annual fee that a mutual fund charges its investors for managing the fund. This fee is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average assets under management (AUM).
- Fund Manager: The fund manager is responsible for making investment decisions for the mutual fund. This person or team conducts research, selects securities, and manages the portfolio to meet the fund’s investment objectives.
- Dividends and Capital Gains: Mutual funds generate income through dividends (from stocks) and interest (from bonds), and they may also realize capital gains from selling securities in the portfolio. These earnings are typically distributed to investors on a regular basis.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds come in a variety of styles and investment objectives, each catering to different risk profiles and financial goals. Here are some of the most common types:
- Equity Funds: Equity mutual funds primarily invest in stocks. These funds are considered higher risk but offer the potential for higher returns. They can be further classified into subcategories based on factors such as market capitalization (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap) or sector focus (technology, healthcare, etc.).
- Bond Funds: Bond mutual funds invest primarily in bonds and other fixed-income securities. These funds tend to be lower risk compared to equity funds but also offer lower returns. They can be an attractive choice for conservative investors looking for income and stability.
- Money Market Funds: Money market mutual funds invest in short-term, low-risk securities such as Treasury bills and certificates of deposit. These funds offer liquidity and are often used by investors seeking a safe place to park their cash, though they typically provide lower returns.
- Balanced Funds: Balanced mutual funds invest in a mix of stocks, bonds, and other asset classes to provide both growth and income. These funds are designed for investors who want a diversified portfolio but are not willing to take on the higher risk of equity funds alone.
- Index Funds: Index mutual funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These funds typically have lower fees because they are passively managed and do not require active decision-making by fund managers.
- Sector Funds: Sector mutual funds focus on specific industries or sectors of the economy, such as technology, healthcare, or energy. These funds can be more volatile because they are concentrated in one area of the market but may offer higher growth potential.
- Target-Date Funds: Target-date funds are designed to automatically adjust their asset allocation based on the target retirement date of the investor. These funds become more conservative as the target date approaches, making them ideal for retirement planning.
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
There are several key advantages to investing in mutual funds that make them an appealing option for investors:
- Diversification: Mutual funds allow investors to gain exposure to a broad range of assets within a single investment, which helps spread risk. Diversification reduces the impact of poor performance in any single security or asset class.
- Professional Management: Mutual funds are managed by experienced professionals who have the expertise to make informed investment decisions. This is especially valuable for investors who do not have the time or knowledge to manage their investments on their own.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are accessible to most investors, with relatively low minimum investment amounts. This makes them an ideal option for beginners and those looking to start investing with limited capital.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds offer liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell their shares at the current NAV on any business day. This provides flexibility for investors who may need to access their funds in the short term.
- Affordability: Mutual funds provide a cost-effective way to invest in a diversified portfolio, as the fees associated with investing in a mutual fund are often lower than those associated with buying individual securities.
Risks of Investing in Mutual Funds
Like all investments, mutual funds come with their own set of risks. It’s important to be aware of these risks before investing:
- Market Risk: The value of mutual fund shares can fluctuate based on market conditions. If the market declines, the value of the fund may also decrease, leading to potential losses.
- Management Risk: Since mutual funds are managed by professionals, there is a risk that poor management decisions can negatively affect the fund’s performance. However, experienced fund managers are more likely to make informed decisions that mitigate this risk.
- Liquidity Risk: While mutual funds are generally considered liquid, some specialized funds (such as real estate or emerging markets) may have less liquidity and may be harder to sell in times of market stress.
- Fee Structure: Some mutual funds have high fees that can eat into long-term returns. It’s important to evaluate a fund’s expense ratio and understand the associated costs before investing.
- Interest Rate Risk: Bond funds, in particular, are sensitive to changes in interest rates. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds may decline, which can affect the performance of bond mutual funds.
How to Choose the Right Mutual Fund
Selecting the right mutual fund depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a mutual fund:
- Investment Goals: Consider your financial objectives—whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a home, or funding your children’s education. This will help you determine which type of mutual fund aligns with your goals.
- Risk Tolerance: Evaluate your risk tolerance. If you are willing to take on more risk for the potential of higher returns, an equity fund may be suitable. Conversely, if you prefer stability and lower risk, bond or money market funds may be better options.
- Fund Performance: While past performance does not guarantee future results, examining the historical performance of a mutual fund can give you insight into how it has performed under different market conditions.
- Fees and Expenses: Compare the expense ratios of different funds. A higher expense ratio can reduce your overall returns, so choose a fund with a reasonable cost structure.
- Fund Manager: Research the experience and track record of the fund manager. A skilled manager can make a significant difference in the fund’s performance over time.
- Fund Size: A fund’s size can influence its ability to perform well. Large funds may struggle to find opportunities for growth, while smaller funds may be more nimble and able to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Also Read: Effective Debt Management Strategies: How To Get Out Of Debt And Build Financial Freedom
Conclusion
Mutual funds are a versatile and accessible investment vehicle that can help you achieve your financial goals through diversification, professional management, and relatively low investment thresholds. By understanding the different types of mutual funds, their benefits, risks, and strategies for selecting the right one, you can build a well-rounded investment portfolio that aligns with your objectives.
FAQs
What is the difference between an actively managed fund and a passively managed fund?
An actively managed fund has a fund manager who makes decisions to try and outperform the market, while a passively managed fund tracks a specific index, such as the S&P 500.
How are mutual fund dividends paid?
Mutual fund dividends are typically paid on a quarterly or annual basis and can either be reinvested into additional shares of the fund or paid out to investors.
Can I invest in mutual funds through my retirement account?
Yes, you can invest in mutual funds through tax-advantaged retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs.
Are mutual funds safe?
While mutual funds are generally considered less risky than individual stocks, they still carry risk, especially in equity or sector funds. Diversifying your investments can help mitigate some of this risk.
How can I redeem my mutual fund shares?
You can redeem mutual fund shares by contacting the fund company or broker, who will then sell your shares at the current NAV.
What is a no-load mutual fund?
A no-load mutual fund does not charge any sales fees or commissions when you buy or sell shares.
Can I invest in international mutual funds?
Yes, there are many mutual funds that invest in international markets, offering exposure to global economies and industries.










